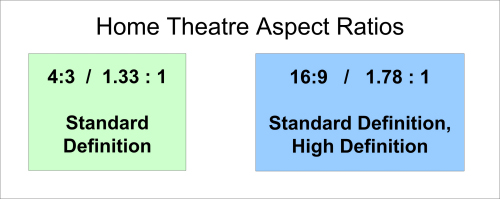
home cinema aspect ratios in comparison (same picture height)
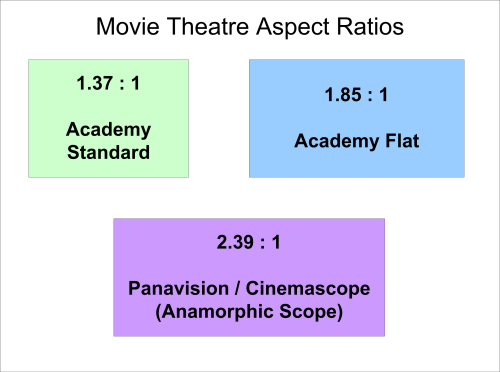
movie theatre aspect ratios in comparison (same picture height)
pixel resolutions in comparison (same pixel size)
aspect ratio comparison (same picture width)
The nominal screen luminance for movie theatres is 16 Foot-Lamberts. It was specified by the SMPTE (Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) as the minimum for film-type movie theatres. The unit Foot-Lamberts is a measurement related to the brightness of a particular image and is equal to 1 lumen per square foot of screen surface. 16 foot-lamberts is chosen because most films have an ideal balance between black and white saturation conditions at this brightness. A tolerance of 20% between the center brightness and a fall-off of at the screen edges is acceptable.
Even for larger cinemas it is often hard to fulfill this requirement.
| Format | Aspect Ratio | Aperture | X : Y | |
| mm | inch | |||
| 16 mm Film | 1.33 | 7.21 x 9.65 | 0.284 x 0.380 | 4 : 3 |
| 35 mm Film (before 1953) | 1.37 | 15.2 x 21 | 0.600 x 0.825 | 4 : 2.92 |
| 35 mm Film (USA) | 1.85 | 11.3 x 21 | 0.446 x 0.825 | 1.85 : 1 |
| 35 mm Film (Europe) | 1.65 | 12.7 x 21 | 0.500 x 0.825 | 1.65 : 1 |
| 35 mm Film (Anamorphic) | 2.35 | 17.8 x 21 | 0.702 x 0.825 | 2.35 : 1 |
| 70 mm Film | 2.21 | 22 x 48.6 | 0.868 x 1.913 | 2.21 : 1 |
| 35 mm Slide (Horizontal) | 1.48 | 22.9 x 34 | 0.902 x 1.340 | 4 : 2.7 |
| 35 mm Slide (Vertical) | 0.68 | 34 x 22.9 | 1.340 x 0.902 | 2.7 : 4 |
| A4 Paper | 1.41 | 210 x 297 | 4 : 2.83 | |
| '8 1/2 x 11' Paper | 1.30 | 215.7 x 279.4 | 8.5 : 11 | |
| Format | Aspect Ratio | Aperture/Resolution | X : Y | |
| mm | pixel | |||
| NTSC Video | 1.33 | 720 × 480 | 4 : 3 | |
| PAL Video | 1.33 | 4 : 3 | ||
| HDTV 720 | 1.78 | 1280 × 720 | 16 : 9 | |
| HDTV 1080 | 1.78 | 1920 × 1080 | 16 : 9 | |
| PAL Wide | 1.78 | 1024 × 576 | 16 : 9 | |
| Letterbox Video | 1.85 | 1.85 : 1 | ||
| "Widescreen" | 1.85 | 1.85 : 1 | ||
| Cinemascope | 2.35 | 2.35 : 1 | ||
| HDV-1 | 1.77 | 1280 x 720 | 16:9 | |
| HDV-2 | 1.77 | 1440 x 1080 | 16:9 | |
| 4K Resolution for Digital Cinema | |||
| Cinema Formats | Horizontal Resolution | Aspect Ratio | Megapixels Per Frame |
| Academy Standard | 3626 x 2664 | 1.37:1 | 9.7 |
| Academy Flat | 3996 x 2160 | 1.85:1 | 8.6 |
| Anamorphic Scope | 4096 x 1714 | 2.39:1 | 7.0 |
| 2K Resolution for Digital Cinema | |||
| Academy Standard | 1828 x 1332 | 1.37:1 | 2.4 |
| Academy Flat | 1998 x 1080 | 1.85:1 | 2.2 |
| Anamorphic Scope | 2048 x 858 | 2.39:1 | 1.8 |


 |
 |
| 1:2.39 picture in a 16:9 screen | 1:1.85 picture in a 16:9 screen |
 | |
| 1:2.39 picture in 4:3 screen | |